Laser Cutting: Difference between revisions
Joshua.Webb (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
(Updated laser cutting guide Autocad with save to PDF instructions) |
||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Laser cutters use high-power laser systems which allow for precise and fast cutting of materials. DBE has 12 laser cutters in total; 2 are technician-operated large format laser cutters, and 10 small-format laser cutters that students can operated once trained. | Laser cutters use high-power laser systems which allow for precise and fast cutting of materials. DBE has 12 laser cutters in total; 2 are technician-operated large format laser cutters, and 10 small-format laser cutters that students can operated once trained. | ||
{{Note | Prepare your files for laser cutting using the information, guides, and templates below. {{Note | ||
| inline = 0 | | inline = 0 | ||
| type = warn | | type = warn | ||
| text = Laser cutting requires a General Makerspace Induction. Use of the Emblaser 2 laser cutters requires a Laser Cutting Badge. | | text = Laser cutting requires a General Makerspace Induction. Use of the Emblaser 2 laser cutters requires a Laser Cutting Badge. | ||
}} | }} | ||
== Laser cutting equipment == | |||
== | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
!Type | !Type | ||
| Line 17: | Line 15: | ||
!Location | !Location | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Trotec SP500 | |Trotec SP500[[File:Trotec sp 500 image.jpg|thumb]] | ||
|1 | |1 | ||
|1245 mm x 710 mm | |1245 mm x 710 mm | ||
| Line 23: | Line 21: | ||
|418 Makerspace | |418 Makerspace | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Darkly Labs Emblaser 2 | |Darkly Labs Emblaser 2[[File:Emblaser 2.png|thumb]] | ||
|10 | |10 | ||
|500mm x 300mm | |500mm x 300mm | ||
| Line 29: | Line 27: | ||
|418 Makerspace | |418 Makerspace | ||
|- | |- | ||
|Trotec Speedy 400 Flexx | |Trotec Speedy 400 Flexx[[File:Speedy 400.jpg|thumb]] | ||
|1 | |1 | ||
|1000 x 610mm | |1000 x 610mm | ||
|Strawboard, plywood, acrylic, mylar, fabrics, and other materials. | |Strawboard, plywood, acrylic, mylar, fabrics, and other materials. | ||
|202 Digital Modelling | |202 Digital Modelling | ||
|} | |}{{Note | ||
| inline = 1 | | inline = 1 | ||
| type = info | | type = info | ||
| Line 44: | Line 41: | ||
== Materials == | == Materials == | ||
{{Note | |||
| inline = 0 | |||
| type = error | |||
| text = The following materials cannot be cut or engraved: <ul><li>Polycarbonate</li><li>PVC (vinyl)</li><li>Anything containing chlorine</li><li>Some metals</li><li>MDF</li><li>Any materials without a Safety Data Sheet (SDS/MSDS)</li><ul> | |||
}} | |||
=== Materials that can be cut and/or engraved === | === Materials that can be cut and/or engraved === | ||
In the '''Makerspace''', you can only process materials supplied by the workshop: | |||
* Plywood 3mm and 6mm thick, up to 1200 x 600mm in size | * Plywood 3mm and 6mm thick, up to 1200 x 600mm in size | ||
* Strawboard 1mm and 2mm thick, up to 900 x 600mm in size | * Strawboard 1mm and 2mm thick, up to 900 x 600mm in size | ||
| Line 55: | Line 54: | ||
You cannot bring in other materials to cut on the Makerspace laser cutters. | You cannot bring in other materials to cut on the Makerspace laser cutters. | ||
In the '''Digital Modelling Workshop''', you can use supplied plywood, strawboard, or acrylic in limited colours, up to 900 x 600mm in size. You can also bring other material that is not stocked, such as: | |||
* Cast acrylic | * Cast acrylic | ||
| Line 62: | Line 61: | ||
* Leather | * Leather | ||
* Card and paper | * Card and paper | ||
* | * Polypropylene | ||
* Acetate | * Acetate | ||
Some materials can be engraved only, including: | |||
* Glass and ceramics | * Glass and ceramics | ||
* Solid wood | * Solid wood | ||
* Some metals | |||
Please discuss using any materials that are not supplied with a technician before bringing them to the workshop. We can recommend suppliers and ensure that you are making an appropriate choice for your project. | |||
=== Material costs === | === Material costs === | ||
Some units require you to | Some units require you to pay a consumables fee, which covers the cost of some or all of your materials. | ||
If your material costs are not covered by a consumables fee, you will need to pay for supplied laser cutting materials at cost price as you use them. | |||
== File Preparation == | == File Preparation == | ||
=== Vector files | === Vector files only === | ||
==== What is a vector file? ==== | |||
A vector graphic file contains a vector image rather than a raster/bitmap image. Vector graphics are constructed of shapes, lines, and points, which do not lose resolution or quality when scaled – think of text in a PDF. | |||
=== | ==== Software that can create vector files ==== | ||
You can create vector files with software that you might already use, such as: | |||
* AutoCAD | |||
* Rhinoceros 3D ("Rhino") | |||
* Adobe Illustrator | |||
* CorelDraw | |||
* Inkscape | |||
Many tutorials for this software are available online. You may also be able to get help using these programs from your tutor or from LinkedIn Learning. | |||
==== Identifying a vector file ==== | |||
Vectors need to be made in your vector program, not just copied and pasted in or imported. If you save your work as a raster format (e.g. psd, jpg, or bmp) it will be rasterized and cannot be converted back into a vector file. If you zoom in on your vector file, you will be able to identify that it does not lose resolution, whereas a raster file will become pixelated or blurry: | |||
[[File:Vector_vs_Raster.jpg|alt=vector vs raster visualisation.|frameless|300x300px]] | |||
=== Size and colour scheme === | |||
Your document/artboard/sheet size should match your material size. Leave a 5mm minimum margin from the edge of your material to your objects. | |||
==== Trotec laser cutters (SP500 and Speedy 400 Flexx) ==== | |||
<span style="background-color: #FF0000">RGB red</span>: cut | |||
<span style="background-color: #00FF00">RGB green</span>: vector engraving (“etching”) | |||
<span style="background-color: #000000;color: #FFFFFF";>RGB black/greyscale</span>: raster engraving | |||
Raster engraving is used to fill areas, either with a single depth/tonality using black or to create gradients, tone, or images, using greyscale. | |||
==== Emblaser 2 ==== | |||
Raster engraving is slightly different. Use the following colour scheme: | |||
== | <span style="background-color: #FF0000">RGB red</span>: cut | ||
<span style="background-color: #00FF00">RGB green</span>: vector engraving (“etching”) | |||
<span style="background-color: #0000FF;color: #FFFFFF";>RGB blue</span>: solid fill raster engraving | |||
= | <span style="background-color: #000000;color: #FFFFFF";>RGB greyscale</span>: raster engraving to produce gradients, tone, or images | ||
All other colours will be ignored. | |||
Cut lines and vector engraving must be lines of the smallest default stroke width possible in your software (e.g. “hairline” or “0.01”), with no fill. | |||
The laser will see '''every''' line in your file, including those hidden under others. For this reason, you need to '''remove any doubled lines''' in your file. Double cut lines can cause damage to your work, material, and the laser cutter. | |||
=== Nesting === | |||
Make sure to keep at least 5mm from the edge of your material, and at least 1mm between shapes. This allows latent heat to disperse from your material, preventing charring and the risk of fires. | |||
Work must be nested to make your cutting times and material use efficient. | |||
=== File size and format === | |||
Export each sheet of material as a '''separate''' PDF at your material size (e.g. 900 x 600mm). | |||
=== | === Examples === | ||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
|+ | |||
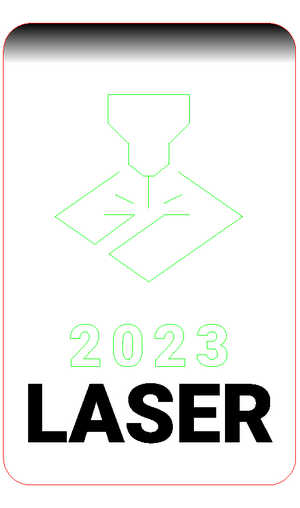
![[File:Laserdemo trotec.png|alt=Artwork prepared for Trotec laser cutters, including cutting (red), vector engraving (green), and raster engraving (black/greyscale). In green is an icon showing a laser beam, and the year 2023. The text "LASER" is in solid black. There is a greyscale gradient at the top, and a red rectangular outline with curved corners.|frameless]] | |||
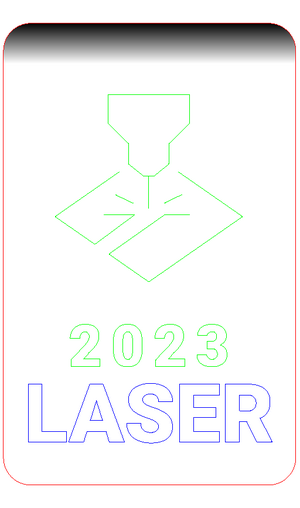
![[File:Laserdemo emb2.png|alt=Artwork prepared for Emblaser 2 laser cutters, including cutting (red), vector engraving (green), and raster engraving (blue/greyscale). In green is an icon showing a laser beam, and the year 2023. The text "LASER" is in a blue outline. There is a greyscale gradient at the top, and a red rectangular outline with curved corners.|frameless]] | |||
|- | |||
|Artwork prepared for Trotec laser cutters, including cutting (red), vector engraving (green), and raster engraving (black/greyscale) | |||
|Artwork prepared for Emblaser 2 laser cutters, including cutting (red), vector engraving (green), and raster engraving (blue/greyscale). | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="2" |[[File:Lasercut logo.jpg|alt=Laser-cut and engraved piece of ply based on example artwork. The ply is rectangular with rounded corners, with a shaded gradient at the top. It has an engraved line drawing of a laser beam, with the words "2023 LASER" engraved below.|center|frameless]] | |||
|- | |||
| colspan="2" |Laser cutting and engraving styles produced by the above image | |||
|} | |||
== Software-specific guides and templates == | |||
=== | === AutoCAD === | ||
[[:File:LASER CUTTING DOC AUTO CAD Jan 2025.pdf|AutoCAD File setup guide (PDF)]] | |||
[[Media:TEMPLATE AutoCAD TORTEC SP500.zip|AutoCAD Laser cutting template Trotec SP500 (dwg)]] | |||
[[ | |||
[[Media:TEMPLATE AutoCAD EMBLASER 2.zip|AutoCAD Laser cutting template Emblaser 2 (dwg)]] | |||
=== | === Rhinoceros 3d === | ||
[[Media:LASER CUTTING DOC DRAFT RHINO 001.zip|Rhino File setup guide (pdf)]] | |||
[[Media:Rhino Laser Cutter Template.zip|Rhino Laser cutting templates (3dm)]] | |||
=== Fusion 360 === | |||
[[Media:Fusion 360 document.pdf|Fusion360 Laser cutting guide (PDF)]] | |||
<gallery> | === Illustrator === | ||
Coming soon<gallery> | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== External Links == | |||
Guide: [https://ms-kb.msd.unimelb.edu.au/the-fablab/laser-cutting/laser-cutting/creating-a-montage-model Creating a Contour Model] by Melbourne School of Design's Fab Lab | |||
[[Category:Digital Fabrication]] | [[Category:Digital Fabrication]] | ||
[[Category:Digital Modelling]] | |||
Latest revision as of 12:03, 17 February 2025
Laser cutters use high-power laser systems which allow for precise and fast cutting of materials. DBE has 12 laser cutters in total; 2 are technician-operated large format laser cutters, and 10 small-format laser cutters that students can operated once trained.
Prepare your files for laser cutting using the information, guides, and templates below.
Laser cutting equipment
Emblaser 2 This equipment can be operated by students who have completed a laser cutting badge. Students must watch the equipment for the entire process.
Materials
- Polycarbonate
- PVC (vinyl)
- Anything containing chlorine
- Some metals
- MDF
- Any materials without a Safety Data Sheet (SDS/MSDS)
Materials that can be cut and/or engraved
In the Makerspace, you can only process materials supplied by the workshop:
- Plywood 3mm and 6mm thick, up to 1200 x 600mm in size
- Strawboard 1mm and 2mm thick, up to 900 x 600mm in size
You cannot bring in other materials to cut on the Makerspace laser cutters.
In the Digital Modelling Workshop, you can use supplied plywood, strawboard, or acrylic in limited colours, up to 900 x 600mm in size. You can also bring other material that is not stocked, such as:
- Cast acrylic
- Wood (thin veneers, plywood, balsa)
- Fabric (natural or acrylic based)
- Leather
- Card and paper
- Polypropylene
- Acetate
Some materials can be engraved only, including:
- Glass and ceramics
- Solid wood
- Some metals
Please discuss using any materials that are not supplied with a technician before bringing them to the workshop. We can recommend suppliers and ensure that you are making an appropriate choice for your project.
Material costs
Some units require you to pay a consumables fee, which covers the cost of some or all of your materials.
If your material costs are not covered by a consumables fee, you will need to pay for supplied laser cutting materials at cost price as you use them.
File Preparation
Vector files only
What is a vector file?
A vector graphic file contains a vector image rather than a raster/bitmap image. Vector graphics are constructed of shapes, lines, and points, which do not lose resolution or quality when scaled – think of text in a PDF.
Software that can create vector files
You can create vector files with software that you might already use, such as:
- AutoCAD
- Rhinoceros 3D ("Rhino")
- Adobe Illustrator
- CorelDraw
- Inkscape
Many tutorials for this software are available online. You may also be able to get help using these programs from your tutor or from LinkedIn Learning.
Identifying a vector file
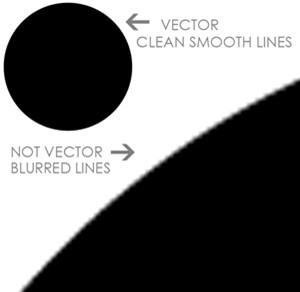
Vectors need to be made in your vector program, not just copied and pasted in or imported. If you save your work as a raster format (e.g. psd, jpg, or bmp) it will be rasterized and cannot be converted back into a vector file. If you zoom in on your vector file, you will be able to identify that it does not lose resolution, whereas a raster file will become pixelated or blurry:
Size and colour scheme
Your document/artboard/sheet size should match your material size. Leave a 5mm minimum margin from the edge of your material to your objects.
Trotec laser cutters (SP500 and Speedy 400 Flexx)
RGB red: cut
RGB green: vector engraving (“etching”)
RGB black/greyscale: raster engraving
Raster engraving is used to fill areas, either with a single depth/tonality using black or to create gradients, tone, or images, using greyscale.
Emblaser 2
Raster engraving is slightly different. Use the following colour scheme:
RGB red: cut
RGB green: vector engraving (“etching”)
RGB blue: solid fill raster engraving
RGB greyscale: raster engraving to produce gradients, tone, or images
All other colours will be ignored.
Cut lines and vector engraving must be lines of the smallest default stroke width possible in your software (e.g. “hairline” or “0.01”), with no fill.
The laser will see every line in your file, including those hidden under others. For this reason, you need to remove any doubled lines in your file. Double cut lines can cause damage to your work, material, and the laser cutter.
Nesting
Make sure to keep at least 5mm from the edge of your material, and at least 1mm between shapes. This allows latent heat to disperse from your material, preventing charring and the risk of fires.
Work must be nested to make your cutting times and material use efficient.
File size and format
Export each sheet of material as a separate PDF at your material size (e.g. 900 x 600mm).
Examples
Software-specific guides and templates
AutoCAD
AutoCAD File setup guide (PDF)
AutoCAD Laser cutting template Trotec SP500 (dwg)
AutoCAD Laser cutting template Emblaser 2 (dwg)
Rhinoceros 3d
Rhino Laser cutting templates (3dm)
Fusion 360
Fusion360 Laser cutting guide (PDF)
Illustrator
Coming soon
External Links
Guide: Creating a Contour Model by Melbourne School of Design's Fab Lab