Laser Cutting: Difference between revisions
Joshua.Webb (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
Joshua.Webb (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Laser cutters use high-power laser systems which allow for precise and fast cutting of materials. DBE has 12 laser cutters in total; 2 are technician-operated large format laser cutters, and 10 small-format laser cutters that students can operated once trained. | Laser cutters use high-power laser systems which allow for precise and fast cutting of materials. DBE has 12 laser cutters in total; 2 are technician-operated large format laser cutters, and 10 small-format laser cutters that students can operated once trained. | ||
| Line 36: | Line 35: | ||
|202 Digital Modelling | |202 Digital Modelling | ||
|} | |} | ||
{{Note | [[File:Trotec sp 500 image.jpg|frameless]][[File:Speedy 400.jpg|frameless|310x310px]][[File:Emblaser_2.png|alt=|frameless|223x223px]]{{Note | ||
| inline = 1 | | inline = 1 | ||
| type = info | | type = info | ||
| Line 80: | Line 79: | ||
== File Preparation == | == File Preparation == | ||
[[File:Vector vs Raster.jpg|alt=vector vs raster visualisation. | [[File:Vector vs Raster.jpg|alt=vector vs raster visualisation.|thumb|300x300px]] | ||
=== Vector files Only === | |||
* Vector files are the only format the laser cutter will recognise for cutting and vector engraving | * Vector files are the only format the laser cutter will recognise for cutting and vector engraving | ||
* A vector file is made up of shapes and lines that do not lose resolution or quality when they are scaled; they use mathematical equations to define shapes and lines | * A vector file is made up of shapes and lines that do not lose resolution or quality when they are scaled; they use mathematical equations to define shapes and lines | ||
| Line 91: | Line 89: | ||
There are slight differences between line colours when preparing files for Trotec (large format) laser cutters and Emblaser (small format) laser cutters. Use the following settings: | There are slight differences between line colours when preparing files for Trotec (large format) laser cutters and Emblaser (small format) laser cutters. Use the following settings: | ||
==== Trotec (SP500 and Speedy 400 Flexx) | ==== Vector Vs Raster ==== | ||
The difference between vector graphics and raster graphics are as follows. Vector graphics use mathematical equations to define shapes and lines, while raster graphics are made up of individual colored pixels arranged in a grid. Therefore, vector graphics can be Infinitely scaled without losing fidelity. | |||
[[File:Types-of-engraving.jpg|alt=Engraving types.|right|frameless|611x611px]] | |||
=== Trotec (SP500 and Speedy 400 Flexx) === | |||
Cut: <span style="color:rgb(255,0,0);font-weight:bold;">RGB red</span>, hairline thickness | Cut: <span style="color:rgb(255,0,0);font-weight:bold;">RGB red</span>, hairline thickness | ||
| Line 98: | Line 101: | ||
Raster engraving: <span style="font-weight:bold;">RGB black</span> or <span style="color:rgb(75,75,75);font-weight:bold;">greyscale</span>; a solid fill engrave should be black fill, while you can use greyscale to create different tonal values or depths | Raster engraving: <span style="font-weight:bold;">RGB black</span> or <span style="color:rgb(75,75,75);font-weight:bold;">greyscale</span>; a solid fill engrave should be black fill, while you can use greyscale to create different tonal values or depths | ||
=== Emblaser 2 === | |||
Cut: <span style="color:rgb(255,0,0);font-weight:bold;">RGB red</span>, hairline thickness | Cut: <span style="color:rgb(255,0,0);font-weight:bold;">RGB red</span>, hairline thickness | ||
| Line 112: | Line 115: | ||
* Your PDF must be the size of your material sheet (e.g. 900 x 600mm for strawboard) | * Your PDF must be the size of your material sheet (e.g. 900 x 600mm for strawboard) | ||
* Save each sheet as a separate PDF file | * Save each sheet as a separate PDF file | ||
== How to set up your files > Software + Templates == | == How to set up your files > Software + Templates == | ||
=== AutoCAD === | |||
[[Media:LASER CUTTING DOC AUTO CAD.zip|AUTOCAD > FILE SET UP GUIDE >]] [[Media:LASER CUTTING DOC AUTO CAD.zip|PDF]] | [[Media:LASER CUTTING DOC AUTO CAD.zip|AUTOCAD > FILE SET UP GUIDE >]] [[Media:LASER CUTTING DOC AUTO CAD.zip|PDF]] | ||
| Line 130: | Line 132: | ||
=== Fusion 360 === | |||
=== Illustrator === | |||
== Setting up files == | == Setting up files == | ||
Revision as of 18:28, 24 June 2024
Laser cutters use high-power laser systems which allow for precise and fast cutting of materials. DBE has 12 laser cutters in total; 2 are technician-operated large format laser cutters, and 10 small-format laser cutters that students can operated once trained.
Prepare your files for laser cutting using the information and guides below.
Equipment Specifications
| Type | Quantity | Dimensions | Materials | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trotec SP500 | 1 | 1245 mm x 710 mm | Strawboard (1 and 2mm), plywood (3 and 6mm) | 418 Makerspace |
| Darkly Labs Emblaser 2 | 10 | 500mm x 300mm | Strawboard (1 and 2mm), plywood (3mm) | 418 Makerspace |
| Trotec Speedy 400 Flexx | 1 | 1000 x 610mm | Strawboard, plywood, acrylic, mylar, fabrics, and other materials. | 202 Digital Modelling |
Emblaser 2 This equipment can be operated by students who have completed a laser cutting badge. Students must watch the equipment for the entire process.
Materials
Materials that can be cut and/or engraved
Both the Makerspace and Digital Modelling Workshop stock plywood and strawboard for laser cutting.
The Makerspace laser cutters cut supplied materials only:
- Plywood 3mm and 6mm thick, up to 1200 x 600mm in size
- Strawboard 1mm and 2mm thick, up to 900 x 600mm in size
You cannot bring in other materials to cut on the Makerspace laser cutters.
The Trotec Speedy 400 Flexx in the Digital Modelling Workshop can cut a wider range of materials, including:
- Cast acrylic
- Wood (thin veneers, plywood, balsa)
- Fabric (natural or acrylic based)
- Leather
- Card and paper
- Polyethylene
- Acetate
And can engrave (but not cut) some others, such as:
- Glass and ceramics
- Solid wood
- Polycarbonate
- PVC (vinyl)
- Anything containing chlorine
- Metals
- MDF
- Any materials without a Safety Data Sheet (SDS/MSDS)
Material costs
Some units require you to a pay a consumables fee, which covers the costs of some or all of your materials. If your material costs are not covered by a consumables fee, you will need to pay for supplied laser cutting materials at cost price.
File Preparation
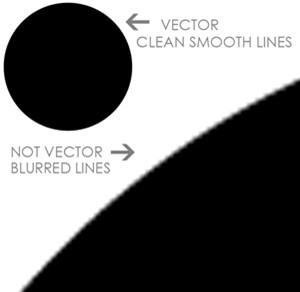
Vector files Only
- Vector files are the only format the laser cutter will recognise for cutting and vector engraving
- A vector file is made up of shapes and lines that do not lose resolution or quality when they are scaled; they use mathematical equations to define shapes and lines
- You can create vector files using programs such as Adobe Illustrator, CorelDraw, Rhino 3D, and AutoCAD, as well as free software like Inkscape.
- Vector files need to be created in a vector program - not just imported or pasted.
Line and shape properties
There are slight differences between line colours when preparing files for Trotec (large format) laser cutters and Emblaser (small format) laser cutters. Use the following settings:
Vector Vs Raster
The difference between vector graphics and raster graphics are as follows. Vector graphics use mathematical equations to define shapes and lines, while raster graphics are made up of individual colored pixels arranged in a grid. Therefore, vector graphics can be Infinitely scaled without losing fidelity.

Trotec (SP500 and Speedy 400 Flexx)
Cut: RGB red, hairline thickness
Vector engraving: RGB green, hairline thickness
Raster engraving: RGB black or greyscale; a solid fill engrave should be black fill, while you can use greyscale to create different tonal values or depths
Emblaser 2
Cut: RGB red, hairline thickness
Vector engraving: RGB green, hairline thickness
Solid fill raster engraving: RGB blue, hairline thickness
Tonal value/gradient: Greyscale
File size and format
- Files must be saved in PDF format
- Your PDF must be the size of your material sheet (e.g. 900 x 600mm for strawboard)
- Save each sheet as a separate PDF file
How to set up your files > Software + Templates
AutoCAD
AUTOCAD > FILE SET UP GUIDE > PDF
AUTOCAD > TEMPLATE > TROTEC SP500 > DWG
AUTOCAD > TEMPLATE > EMBLASER2 > DWG
Rhino 3d
RHINO > FILE SET UP GUIDE > PDF
Fusion 360
Illustrator
Setting up files
Autodesk Fusion 360
Autodesk Fusion 360 combines CAD, CAM, CAE, and PCB into a single, integrated cloud software platform. It includes all the tools that you need to go from design to manufacturing, seamlessly.
Laser Cutting Setup
The golden rule in Fusion is that you make sections of your models as components. This approach involves organising different sections of a model as separate components, each containing essential data such as sketch information, bodies, and origin planes. This concept can be likened to layers in software applications like AutoCAD or Photoshop.
Example of component-based modelling
Let's say you want to laser cut a 3mm Polar ply box with connecting finger joints. Using the inspect menu, you can select "Display Component Colors" to visually seen each component with a distinct colour ID. To prepare the design for laser cutting:
- Selecting the top-level component
- Creating a new sketch
- Draw a rectangle using the create menu or simply hit the [R] key
- Select Center Point rectangle
- Define your size, switching between height and width with [Tab➡] key
- Hit enter and then finish sketch
- Ensure the plane is at the bottom of your model.
- Select Arrange in Modify menu with all the components selected, or select them individually afterward.
- Make sure all components are selected and appear in Arrange options.
- Finally, select envelope on the plane to arrange the objects flat.
-
How to display component colors using the inspect menu.
-
Define your size, switching between height and width with [Tab➡] key



![Define your size, switching between height and width with [Tab➡] key](/images/thumb/8/8a/5._Defining_the_size.png/120px-5._Defining_the_size.png)